TNM
Categories |
FIGO
Stages |
|
|---|
| TX | | Primary tumour cannot be assessed |
T0
| | No evidence of primary tumour
|
Tis٭
| | Carcinoma in situ (preinvasive carcinoma)
|
T1
| I
| Cervical carcinoma confined to uterus (extension to corpus should be disregarded)
|
T1a٭٭
| IA
| Invasive carcinoma diagnosed only by microscopy. Stromal invasion with a maximum depth of 5 mm measured from the base of the epithelium and a horizontal spread of 7 mm or less. Vascular space involvement, venous or lymphatic, does not affect classification.
|
T1a1
| IA1
| Measured stromal invasion of 3.0mm or less in depth and 7.0mm or less in horizontal spread
|
T1a2
| IA2
| Measured stromal invasion of more than 3.0 mm and not more than 5.0 mm with a horizontal spread 7.0 mm or less
|
T1b
| IB
| Clinically visible lesions confined to the cervix or microscopic lesion greater than T1a/IA2. Includes all macroscopically visible lesions, even those with superficial invasion.
|
T1b1
| IB1
| Clinically visible lesion 4.0 cm or less in greatest dimension
|
T1b2
| IB2
| Clinically visible lesion more than 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
|
T2
| II
| Cervical carcinoma invading beyond the uterus but not to the pelvic wall or to lower third of the vagina
|
T2a
| IIA
| Tumour without parametrial invasion
|
T2a1
| IIA1
| Clinically visible lesion 4.0 cm or less in greatest dimension
|
T2a2
| IIA2
| Clinically visible lesion more than 4.0 cm in greatest dimension
|
T2b
| IIB
| Tumour with parametrial invasion
|
T3
| III
| Tumour extending to pelvic sidewall* and/or involving lower third of vagina and/or causing hydronephrosis or non-functioning kidney
*Pelvic sidewall is defined as the muscle, fascia, neurovascular structures and skeletal portions of the bony pelvis. On rectal examination there is no cancer free space between the tumour and the pelvic sidewall |
T3a
| IIIA
| Tumour involving lower third of vagina but not extending to pelvic wall
|
T3b
| IIIB
| Tumour extending to pelvic wall and/or causing hydronephrosis or non-functioning kidney
|
T4
| IVA
| Tumour invading mucosa of bladder or rectum and/or extending beyond true pelvis
Note: the presence of bullous edema is not sufficient to classify a tumour as T4
|
TNM
Categories | FIGO
Stages |
|
|---|
NX
|
| Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
|
N0
|
| No regional lymph node metastasis
|
N0(i+)
|
| Isolated tumour cells in regional lymph nodes no greater than 0.2 mm
|
N1
| IIIB
| Regional lymph node metastasis
|
M0
|
| No distant metastasis
|
M1
| IVB
| Distant metastasis (including peritoneal spread, involvement of supraclavicular, mediastinal, or paraaortic lymph nodes, lung, liver, or bone)
|
*FIGO no longer includes stage 0 (Tis)
٭٭All macroscopically visible lesions—even with superficial invasion—are T1b/IB.
Anatomic stage/prognostic groups (FIGO 2008)
|
|---|
Stage 0*
| Tis
| N0
| M0
|
Stage I
| T1
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IA
| T1a
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IA1
| T1a1
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IA2
| T1a2
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IB
| T1b
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IB1
| T1b1
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IB2
| T1b2
| N0
| M0
|
Stage II
| T2
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IIA
| T2a
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IIA1
| T2a1
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IIA2
| T2a2
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IIB
| T2b
| N0
| M0
|
Stage III
| T3
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IIIA
| T3a
| N0
| M0
|
Stage IIIB
| T3b | Any N
| M0
|
| T1-3
| N1
| M0
|
Stage IVA
| T4
| Any N
| M0
|
Stage IVB
| Any T
| Any N
| M0
|
View a
larger version of the Cervix Staging Diagram.
Following biopsy confirmation of carcinoma of the cervix, history and physical examination and the following staging investigations should be done:
- Lab studies: CBC, differential, BUN and creatinine, liver function tests and β-HCG in pre-menopausal patients, as indicated.
-
Radiological studies: MRI pelvis and PET-CT scan for select patients with early stage cervical cancer
(Management Algorithm - click on image below to enlarge). CT scan of the chest-abdomen-pelvis can be done if PET scan is not available. PET-scan and MRI of the pelvis are standard of care before starting radiotherapy (for staging and planning purposes)
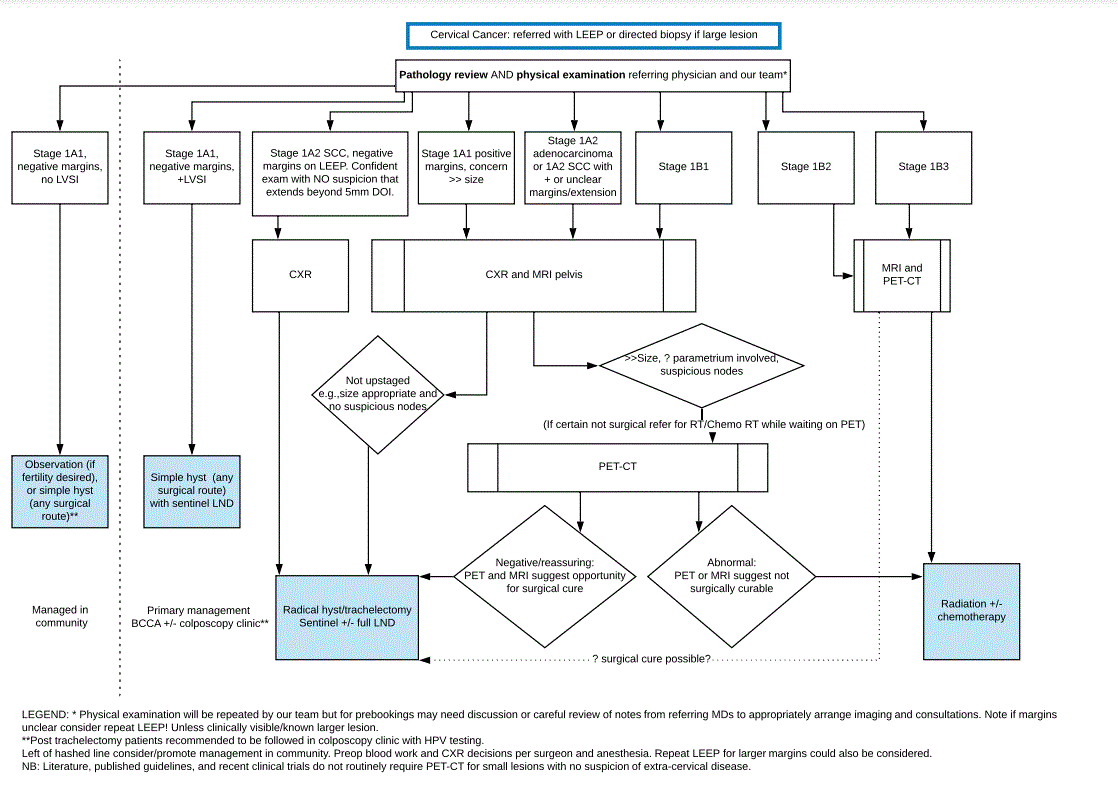
- Examination under anesthesia (EUA), if necessary, to assess primary tumour volume and extent.